Introduction To Indian Geography
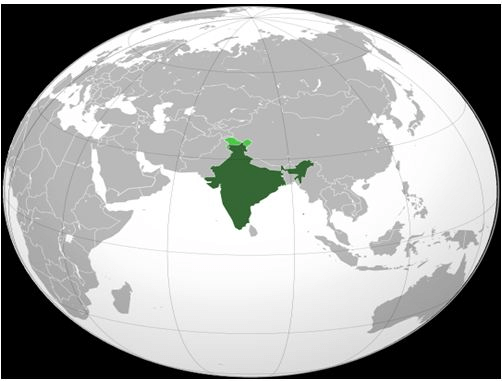 India: Location And Size
India: Location And Size
Location
- India is a vast country. Lying entirely in the Northern hemisphere, the main land extends between latitudes 8°4’N and 37°6’N and longitudes 68°7’E and 97°25’E.
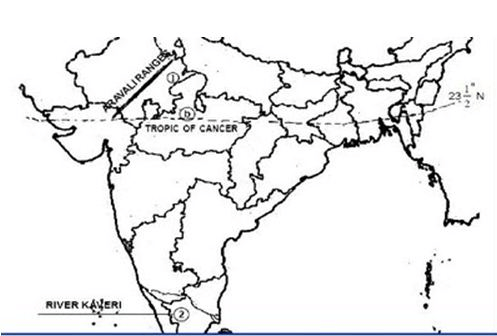
- The Tropic of Cancer (23° 30’N) divides the country into almost two equal parts.
- To the southeast and southwest of the mainland, lie the Andaman and Nicobar islands and the Lakshadweep islands in Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea respectively.
Size
- Geography Area of India : 32,87,263 sq. km.
- It accounts for 2.4% of the total world area and roughly 16% of the world population.
- India is the seventh largest country of the world.
- India has a land boundary of about 15,200 km and the total length of the coast line of the mainland including Andaman and Nicobar and Lakshadweep is 7,516.6 km.
India’s Neighbours
- India occupies an important strategic position in South Asia.
- India shares its land boundaries with Pakistan and Afghanistan in the northwest China , Nepal and Bhutan in the north and Myanmar and Bangladesh in the east.
- Our southern neighbours across the sea consist of the two island countries, namely Sri Lanka and Maldives.
- Sri Lanka is separated from India by a narrow channel of sea formed by the Palk Strait and the Gulf of Mannar while Maldives Islands are situated to the south of the Lakshadweep Islands.
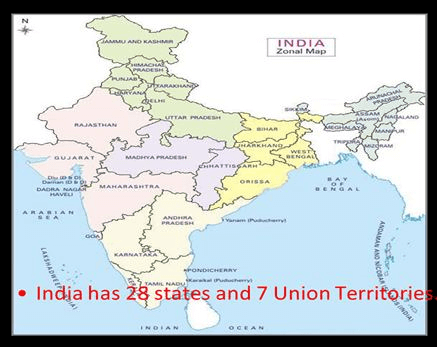
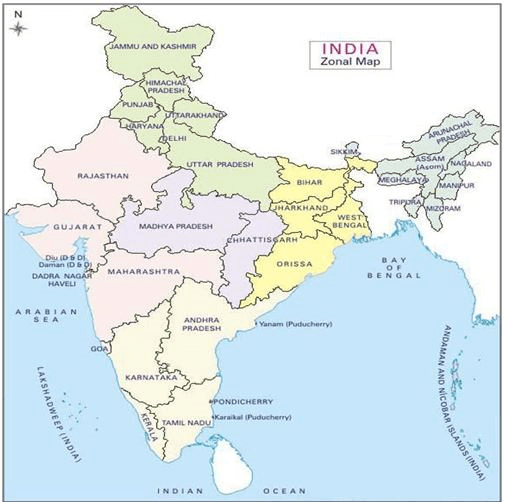
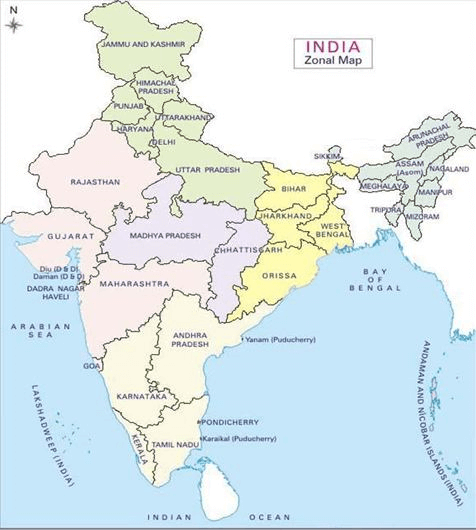
Facts about position of states
UP borders the maximum number of States-8 (Uttarakhand, HP, Haryana, Rajasthan, MP, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Bihar). After UP is Assam, which touches the border of 7 States
Tropic of Cancer passes through 8 States : Gujarat, Rajasthan, MP, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, WB, Tripuro, Mizoram
- Indian Standard Meridian passes through 5 States : UP, MP, Chhattisgarh, Orissa, AP.
- 9 States form the coast of India. They are : Gujarat, Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu. Andhra Pradesh, Orissa and West Bengal.
- 2 Union Territories, viz. Daman & Diu and Pondicherry are also on the coast.
- The Union Territories of Andaman and Nicobar Islands and Lakshadweep are made up of islands only.
Comments
Post a Comment